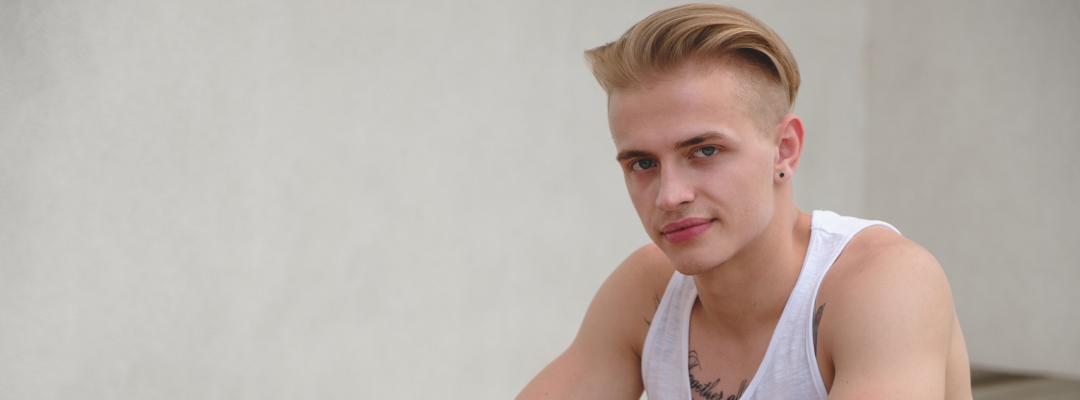
Facial masculinization is a set of procedures designed to give the face characteristics that are socially associated with masculine traits. For many trans men and non-binary people assigned female at birth, these changes can be an important part of their gender affirmation process, as they help their external image reflect their true identity. Here we explain everything you need to know about facial masculinization FTM – Female To Male.
Basically, there are three main ways to achieve masculinization in transgender men: changes derived from testosterone hormone therapy, facial masculinization surgeries, and certain aesthetic medicine treatments. Each has different goals, results, and timelines, and they can be combined to achieve a balanced and harmonious outcome.
Characteristics of the male face
To better understand what a trans man or non-binary person seeks when wanting a more masculine face, we need to know what is considered a male face.
The face of a cisgender man presents a series of traits that differentiate it from a female face. This is the result of what we understand as sexual dimorphism and the influence of hormones such as testosterone in men. In general, male faces have a more robust and defined bone structure, such as:
-
- A wider, more angular jaw, with defined angles and a more projected chin.
- A straighter or slightly backward-sloping forehead, with more prominent supraorbital ridges.
- A hairline that is further back and M-shaped.
- Smaller eyes and “squarer” faces; male skulls have squarer and lower orbits.
- Cheekbones that are less projected forward and located lower compared to female faces.
- A wider and straighter nose, often with a slight dorsal hump.
- Thinner lips that are less everted (turned outward).
- Thicker and firmer skin, as a consequence of hormones.
- Facial hair (beard and mustache) and less fat accumulation in the cheeks, due to the effects of testosterone.
Although some of these characteristics can be achieved through hormone therapy (such as facial hair or fat redistribution), knowing them is essential when planning any facial masculinization surgery or aesthetic medicine treatment to achieve a natural and harmonious result. It is also important to have realistic expectations about what can and cannot be achieved with different facial masculinization procedures.
Facial Masculinization with hormone therapy
Testosterone hormone therapy causes gradual changes in facial structure and appearance. These changes are most noticeable during the first years of treatment and are maintained long term. The most common effects of hormone therapy include:
-
- Increase in facial muscle mass: testosterone stimulates muscle tissue growth and can give a more robust appearance to the jaw and neck.
- Redistribution of facial fat: the face tends to lose fat in the cheeks and cheekbones, highlighting angles and reducing the typical roundness of a feminine face.
- Changes in the skin: the skin becomes thicker and, in some cases, oilier.
- Facial hair growth: beard and mustache growth, which develops gradually and may take several years to reach maximum density.
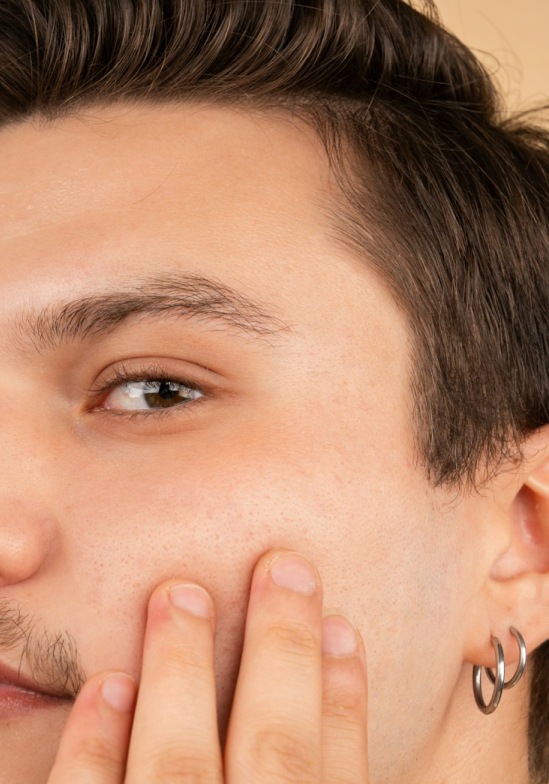

Facial masculinization surgery
When hormone therapy is not enough to achieve the desired result, facial masculinization surgery in trans men can directly modify bone structure and soft tissues to create a more masculine appearance. Some of the facial masculinization surgeries that can be performed include:
Jaw Enhancement and Definition
Implants or osteotomy techniques are used to widen the mandibular angle, project the chin, and give more definition to the jawline. A broader chin and a well-defined jawline are traits often associated with a masculine face.
Chin Augmentation
Chin augmentation can be achieved with implants or by advancing the chin bone. A projected chin helps balance the facial profile and achieve a masculine expression that conveys strength.
Nose Surgery
Masculinization rhinoplasty aims for a straighter nose or one with a slight dorsal hump, and a wider bridge, always respecting the overall harmony of the face.
These surgeries can be performed individually or in combination, depending on each person’s needs and goals. If you are considering this type of plastic surgery, choose a team experienced in gender surgery to achieve a natural and proportionate result.
Facial masculinization fillers
Aesthetic medicine offers non-surgical options for masculinizing the face. They are less invasive, provide immediate or short-term results, and can be an alternative or complement to surgery.
Treatments such as dermal fillers with hyaluronic acid, which are used to widen the jaw, project the chin, or enhance the cheekbones, are among the most requested. However, it should be taken into account that these are temporary, usually lasting between 12 and 18 months. Other treatments such as biostimulators, neuromodulators, chemical peels, microneedling, etc., can help highlight bone structure as well as achieve a more masculine skin texture.
Hormone therapy, surgery, or aesthetic medicine?
Hormone therapy, facial masculinization surgery, or aesthetic medicine – which one to choose? The most important thing is to have clear expectations and goals, and to consult with a medical team experienced in masculinization for trans patients.
It should be noted that testosterone hormone therapy provides natural and progressive changes but does not alter bones. Facial masculinization surgery transforms the bone structure for a permanent change, while aesthetic medicine offers subtle and temporary modifications.
In many cases, the most advisable approach is a combination. That is, begin hormone therapy and allow it to act for at least 1–2 years to assess the extent of natural changes. After that, aesthetic medicine can be considered – for example, a broader chin or a more defined jaw. Surgery can then be pursued for structural and permanent changes once the final goal is clear.
Facial masculinization female to male: A personal decision
Facial masculinization FTM is a personal decision that must be assessed individually in each case. It is advisable for trans men or non-binary people who want more typically masculine facial traits to wait about two years after starting hormone therapy, if they have chosen this treatment as part of their transition.
However, it should be remembered that although testosterone produces significant changes in skin, fat, and facial hair, it does not affect bone structure. This aspect can only be modified through surgery.
Do you need more information about facial masculinization in trans men?
Contact the IM GENDER team to get your questions answered with personalized guidance.